3.5. 为 Container 添加健康检查方法

kustz 终于到了准生产的地步了。 今天的健康检查接口, 就为我们解决这个问题。
我们要知道, 确定一个应用能不能对外提供服务之前, 需要进行一个 可用性 检测。 而这个检测通常被我们称为 健康检查。
Kubernetes 的健康检查
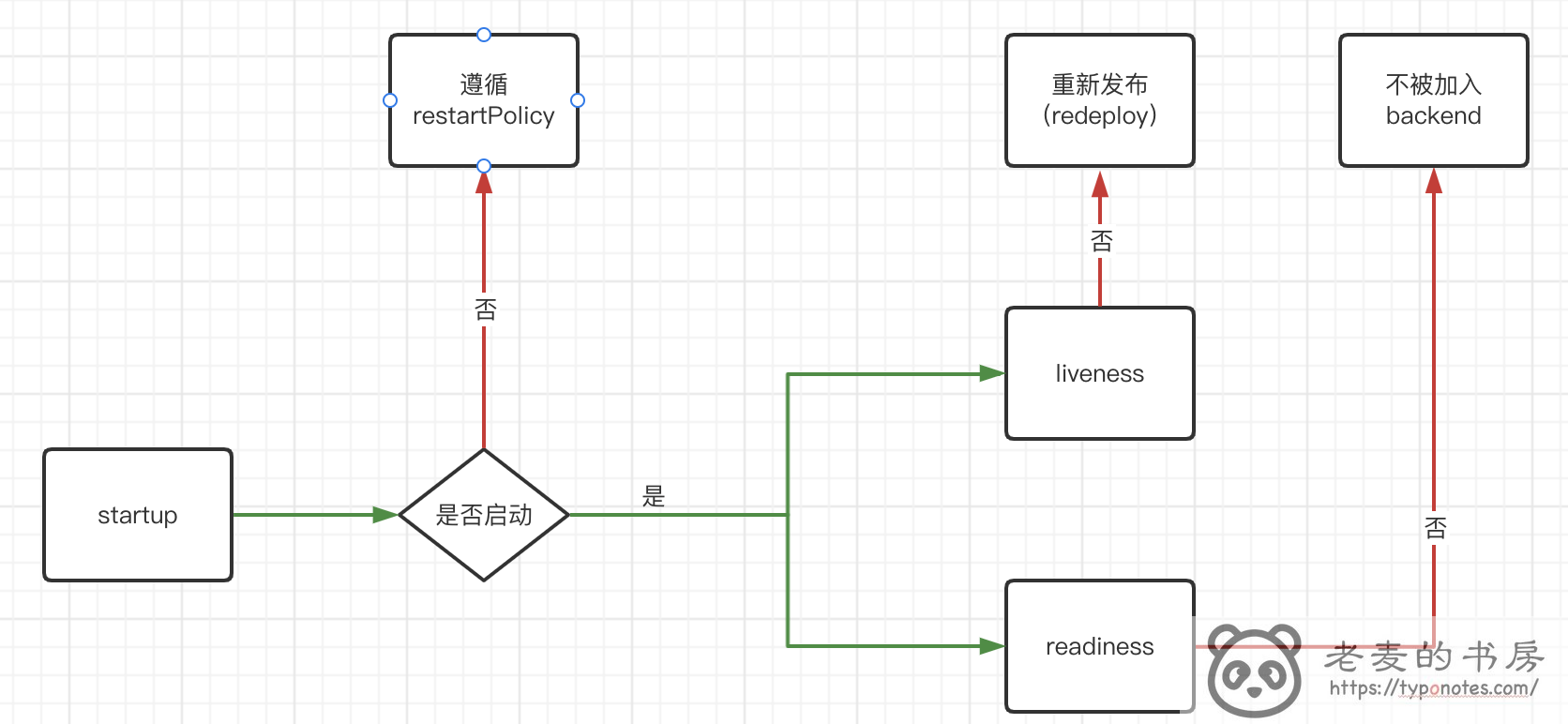
在 Kubernetes 中, 为我们提供了 主要 的 3类状态 的健康检查。
- startup: 等待探针。 如果执行成功, 则再执行 liveness, readienss。 如果执行失败, 则遵循
restartPolicy 规则。 - liveness: 存活探针, 如果失败, 服务将被重新发布(redeploy)。
- readiness: 就绪探针, 如果失败, 服务不会加入到 service backend endpoints 中对外提供服务。
https://kubebyexample.com/learning-paths/application-development-kubernetes/lesson-4-customize-deployments-application-2
此外, Kubernetes 支持 4种类型 的检查方式
- httpGet: 检查 GET 接口返回值。
- tcp: tcp 端口是否打开。
- exec: 命令执行是否成功。
- grpc: grpc 端口是否打开。
kustz.yml 配置
一如既往, 我们需要抽象一个简单明了的方法定义健康检查方法。 剩下的就交给 kustz 处理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| # kustz.yml
service:
probes:
liveness:
action: http://:8080/healthy
headers:
token: "token123"
initialDelaySeconds: 30
readiness:
action: tcp://0.0.0.0:8080
startup:
action: cat /tmp/healthy
|
从配置中可以看到, 通过 action 我们提供了其中三种检查方法 httpGet, tcp, exec。
grpc 现在还属于 1.24 还 beta 状态。 对于 grpc 我也不熟, 所以就不讨论了。
编码
这节不难
数据结构定义
对应的在 /pkg/kustz/kustz.go 中添加如下结构。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| type Service struct {
Probes ContainerProbes `json:"probes,omitempty"`
}
type ContainerProbe struct {
ProbeHandler `json:",inline"`
InitialDelaySeconds int32 `json:"initialDelaySeconds,omitempty"`
TimeoutSeconds int32 `json:"timeoutSeconds,omitempty"`
PeriodSeconds int32 `json:"periodSeconds,omitempty"`
SuccessThreshold int32 `json:"successThreshold,omitempty"`
FailureThreshold int32 `json:"failureThreshold,omitempty"`
TerminationGracePeriodSeconds *int64 `json:"terminationGracePeriodSeconds,omitempty"`
}
|
其中 ContainerProbe 基本上就是从 corev1.Probe 中直接复制过来的, 但又对 ProbeHandler 进行了一些本地化处理。
1
2
3
4
| type ProbeHandler struct {
Action string `json:"action,omitempty"`
Headers map[string]string `json:"headers,omitempty"`
}
|
处理 Action 生成 Handler
对于 Action 的值, 我们需要进行类型处理, 并返回相应的 corev1.ProbeHandler。
在 /pkg/tokube/container_probe.go 中, 定义函数 ProbeHandler 处理 action 和 headers 的值并返回结果。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| // ProbeHandler action
//
// http(s)://:8080/healthy
// tcp://:8080
// cat /tmp/healthy
func ProbeHandler(action string, headers map[string]string) corev1.ProbeHandler {
if strings.HasPrefix(action, "tcp://") {
return toTCPProbeHandler(action)
}
if strings.HasPrefix(action, "http://") || strings.HasSuffix(action, "https://") {
return toHTTPProbeHandler(action, headers)
}
return toExecProbeHandler(action)
}
|
可以看到, 通过判断 action 的前缀字符串的值, 确认了健康检查的方法。 而只有 httpGet 方法接受了 headers 参数。
在 toTCPProbeHandler() 和 toHTTPProbeHandler() 中, 使用 url.Parse() 方法, 很简单的提取了所有字段数据。
在 toExecProbeHandler 中, 直接使用 strings.Split() 方法分割。
为 Container 添加健康检查
在 /pkg/kustz/k_container.go 中, 为 ContainerProbe 为添加方法 kubeProbe 创建健康检查, 这时添加所有附加参数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| // kubeProbe return Kube Probe without handler
func (cp *ContainerProbe) kubeProbe() *corev1.Probe {
handler := tokube.ProbeHandler(cp.Action, cp.Headers)
return &corev1.Probe{
ProbeHandler: handler,
InitialDelaySeconds: cp.InitialDelaySeconds,
TimeoutSeconds: cp.TimeoutSeconds,
PeriodSeconds: cp.PeriodSeconds,
SuccessThreshold: cp.SuccessThreshold,
FailureThreshold: cp.FailureThreshold,
TerminationGracePeriodSeconds: cp.TerminationGracePeriodSeconds,
}
}
|
为 ContainerProbes 添加 kubeProbe 方法, 解决 ContainerProbe 的为 nil 的问题。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| func (cps ContainerProbes) kubeProbe(cp *ContainerProbe) *corev1.Probe {
if cp == nil {
return nil
}
return cp.kubeProbe()
}
|
测试
执行命令, 检查结果




