ansible synchronize 同步文件夹
使用 ansible
synchronize_module
可以控制机和目标机之间同步目录
1
2
3
4
| cat /root/ansible_copy/hosts
[backup]
10.1.1.1 serverid=1001 ansible_ssh_user=backup_user ansible_ssh_port=22
|
- 通过 mode 控制同步方向
- mode=push 默认值。 从『控制机』到『目标机』
- mode=pull 从『目标机』到『控制机』
推送 push
1
2
3
| ansible -i /root/ansible_copy/hosts backup -m synchronize -a 'src=/tmp/svr_01/backup/ dest=/tmp/svr_02/backup/'
ansible -i /root/ansible_copy/hosts backup -m synchronize -a 'mode=push src=/tmp/svr_01/backup/ dest=/tmp/svr_02/backup/'
|
拉取 pull
1
| ansible -i /root/ansible_copy/hosts backup -m synchronize -a 'mode=pull src=/tmp/svr_01/backup/ dest=/tmp/svr_02/backup/'
|
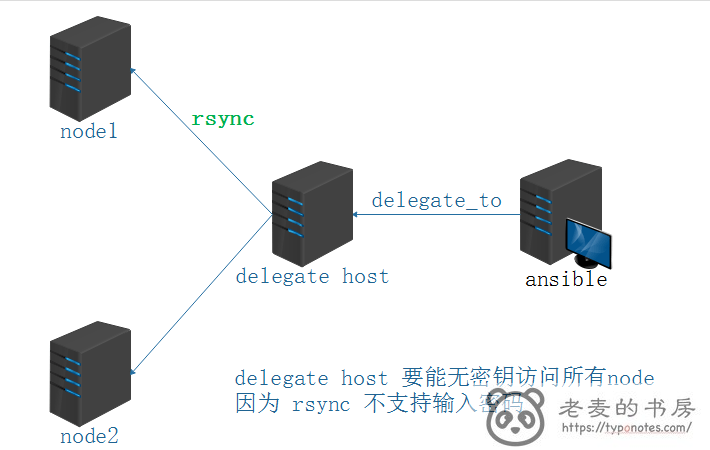
delegate_to 授权
需要注意的是,使用 delegate_to 授权机进行 synchronize 。需要保证授权机能密钥访问远程机。
因为 delegate_to 时,使用的帐户权限是授权机的,而非 ansible host 的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| # Synchronization of src on delegate host to dest on the current inventory host.
# 同步『授权机(delegate host)』的 src 目录到远程机器
# 注:需要指定 rsync_opts。
# 参考 https://github.com/ansible/ansible/issues/7250
- synchronize:
src: /first/absolute/path
dest: /second/absolute/path
rsync_opts: '-e "ssh -p {{ ansible_ssh_port }} -i /home/delegate_host_user/.ssh/id_rsa"'
delegate_to: delegate.host
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
---
# synchronize
- name: sync local folder to remote host
hosts: server01
tasks:
- name: push local folder to remote host
synchronize:
src: /tmp/sync_folder/
dest: /tmp/sync_folder/
rsync_opts: '-e "ssh -p {{ ansible_ssh_port }} -i /home/server02/.ssh/id_rsa"'
delegate_to: server02
|
playbook 更多高级选项
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
|
# Synchronization of src on the control machine to dest on the remote hosts
# 同步控制机的 src 到目标机的 dest
- synchronize:
src: some/relative/path
dest: /some/absolute/path
# Synchronization using rsync protocol (push)
# 使用 rsync 协议同步(推送)
- synchronize:
src: some/relative/path/
dest: rsync://somehost.com/path/
# Synchronization using rsync protocol (pull)
# 使用 rsync 协议同步(拉取)
- synchronize:
mode: pull
src: rsync://somehost.com/path/
dest: /some/absolute/path/
# Synchronization using rsync protocol on delegate host (push)
- synchronize:
src: /some/absolute/path/
dest: rsync://somehost.com/path/
delegate_to: delegate.host
# Synchronization using rsync protocol on delegate host (pull)
- synchronize:
mode: pull
src: rsync://somehost.com/path/
dest: /some/absolute/path/
delegate_to: delegate.host
# Synchronization without any --archive options enabled
# 不使用 --archive (归档) 选项 同步
- synchronize:
src: some/relative/path
dest: /some/absolute/path
archive: no
# Synchronization with --archive options enabled except for --recursive
# 使用不包含 --recursive (递归) 的 --archive 选项 同步
- synchronize:
src: some/relative/path
dest: /some/absolute/path
recursive: no
# Synchronization with --archive options enabled except for --times, with --checksum option enabled
# 使用不包含 --times 的 --archive 选项,并使用 --checksum 校验选项 同步。
- synchronize:
src: some/relative/path
dest: /some/absolute/path
checksum: yes
times: no
# Synchronization without --archive options enabled except use --links
- synchronize:
src: some/relative/path
dest: /some/absolute/path
archive: no
links: yes
# Synchronization of two paths both on the control machine
# 在控制机本地同步两个目录
- synchronize:
src: some/relative/path
dest: /some/absolute/path
delegate_to: localhost
# Synchronization of src on the inventory host to the dest on the localhost in pull mode
# 使用 pull 模式, 同步当前 inventory 中的目标机的 src 到控制机本地的 dest。
- synchronize:
mode: pull
src: some/relative/path
dest: /some/absolute/path
# Synchronization of src on delegate host to dest on the current inventory host.
# 同步『授权机(delegate host)』的 src 目录到远程机器
# 注:需要指定 rsync_opts。
# 参考 https://github.com/ansible/ansible/issues/7250
- synchronize:
src: /first/absolute/path
dest: /second/absolute/path
rsync_opts: '-e "ssh -p {{ ansible_ssh_port }} -i /home/delegate_host_user/.ssh/id_rsa"'
delegate_to: delegate.host
# Synchronize two directories on one remote host.
# 同步『授权机器』上的两个目录同步
# 实际上,需要授权本机访问本机
- synchronize:
src: /first/absolute/path
dest: /second/absolute/path
delegate_to: "{{ inventory_hostname }}"
# 因此不如使用 shell 模块
# 参考 http://www.adelson.co/ansible-sync-delegate.html
- shell: rsync --arHz /first/absolute/path /second/absolute/path
# Synchronize and delete files in dest on the remote host that are not found in src of localhost.
# 同步本地 src 到目标机 dest,并删除本地 src 中没有的文件
- synchronize:
src: some/relative/path
dest: /some/absolute/path
delete: yes
recursive: yes
# Synchronize using an alternate rsync command
# This specific command is granted su privileges on the destination
# 该命令需要在目标机上有『su 权限』
- synchronize:
src: some/relative/path
dest: /some/absolute/path
rsync_path: "su -c rsync"
# Example .rsync-filter file in the source directory
# - var # exclude any path whose last part is 'var'
# - /var # exclude any path starting with 'var' starting at the source directory
# + /var/conf # include /var/conf even though it was previously excluded
# Example .rsync-filter file in the source directory
# - var # 排除任何以 'var' 结尾的路径
# - /var # 排除任何以 'var' 开始的路径
# + /var/conf # 包含 /var/conf 即使在之前被指定排除
# Synchronize passing in extra rsync options
- synchronize:
src: /tmp/helloworld
dest: /var/www/helloworld
rsync_opts:
- "--no-motd"
- "--exclude=.git"
|
Notes
- rsync 必须状态本机与目标机.
- For the synchronize module, the “local host” is 同步的发起方, and the “destination host” is 同步的接收方.
- 可以使用
delegate_to 改变 “local host” . 该功能可以实现在两台远程机器上同步,或者在一台远程机器上执行两个目录的同步。 - synchronize src 所使用的
用户 和 权限 是在本机发起 Ansible 任务的用户的权限(或者是使用 delegate_to 时,授权机上的 remote_user) - synchronize dest 所使用的
用户 和 权限 是目标机上的 remote_user 的用户权限;或者为使用 become=yes 时的 become_user 的权限。 - In 2.0.0.0 a bug in the synchronize module made become occur on the “local host”. This was fixed in 2.0.1.
- 目前, synchronize 被限制使用无密码 sudo 提权。这是因为通过 rsync 连接到远程机器,且 rsync 并未提供任何使用 sudo 方式的接口。
- 同步策略决定了目前只有少部分连接 (ssh, paramiko, local, and docker) 方式支持 synchronize。 Note that the connection for these must not need a password as rsync itself is making the connection and rsync does not provide us a way to pass a password to the connection.
- Expect that
dest=~/x will be ~<remote_user>/x even if using sudo. - Inspect the verbose output to validate the destination user/host/path are what was expected.
- To exclude files and directories from being synchronized, you may add
.rsync-filter files to the source directory. - rsync daemon must be up and running with correct permission when using rsync protocol in source or destination path.
- The synchronize module forces
--delay-updates to avoid leaving a destination in a broken in-between state if the underlying rsync process encounters an error. Those synchronizing large numbers of files that are willing to trade safety for performance should call rsync directly.



